Key takeaways
Ozempic requires gradual dose increases to minimize side effects and needs to be taken on the same day each week.
Patients taking Ozempic need to rotate their injection sites in order to prevent skin irritation or infection.
Using an Ozempic dosage chart to log your doses and injection sites makes it easier to follow your treatment plan.
Ozempic (semaglutide) is a prescription injectable medication that was initially approved to treat Type 2 diabetes. Since its initial approval, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved two additional indications: to reduce the risk of adverse cardiovascular events in adults with Type 2 diabetes and heart disease and to reduce worsening of kidney disease in adults with Type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Ozempic is in the family of medications known as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, which mimic a hormone to help lower blood sugar levels in the body. Since it also reduces appetite and calorie intake, it is commonly prescribed off-label to achieve weight loss.
Healthcare providers determine what dosage of Ozempic to prescribe based on which condition it is intended to treat, the patient’s treatment goals, and how well the patient is responding to the medication. Because Ozempic requires titration (increasing dosage over time), having a chart to track your dosage can be convenient.
Ozempic dosage
The recommended starting dose of Ozempic is 0.25 milligrams (mg) injected subcutaneously (under the skin) once a week for the first four weeks. The dosage can then be increased to the standard dosage of 0.5 mg once weekly. A gradual increase in dosage helps the body adjust to the medication and reduces the risk of side effects.
If blood sugar levels in Type 2 diabetes patients remain uncontrolled at 0.5 mg per week for four weeks, their healthcare provider may increase the dosage to 1 mg once weekly. The same is true for patients with chronic kidney disease. After four weeks on the 1 mg dose, the dosage may be increased again to 2 mg if needed for further glycemic control in patients with Type 2 diabetes. The maximum dose should not exceed 2 mg once per week.
Adjustments in dosage may be needed based on blood sugar levels, including your A1C levels. The A1C level shows how well blood sugar has been controlled every moment of every day over the past 90 days. Your healthcare provider may recommend regular lab visits to monitor your condition.
Below is an overview of what an initial Ozempic dosing schedule might look like. Your healthcare provider will prescribe a dosing schedule that’s right for you. Always follow your healthcare provider’s guidance. Never change your dosage without consulting them first.
Ozempic dosage chart |
||
|---|---|---|
| Month # | Dose | Frequency |
| Month 1 | 0.25 mg | Once per week |
| Month 2 | 0.5 mg | Once per week |
| Month 3 | 1 mg | Once per week |
| Month 4 and beyond | 2 mg | Once per week |
Ozempic dosage for weight loss vs. diabetes
The above dosages are the FDA-approved dosages to help manage diabetes mellitus. If an individual has Type 2 diabetes and is overweight or has obesity, the dosage may be the same. If a healthcare provider prescribes Ozempic off-label solely for weight loss, they may or may not recommend a different dosing schedule.
In any case, there’s no standard Ozempic dosage for weight loss since the drug is not FDA approved for this purpose. For weight loss alone, a healthcare provider may recommend Wegovy, which has the same active ingredient (semaglutide) as Ozempic but is specifically approved for weight loss. Wegovy pens come in different strengths than Ozempic. While the initial starting dosage of Wegovy is 0.25 mg once weekly for four weeks, the target dosage is 1.7 mg or 2.4 mg once weekly.
RELATED: Wegovy vs. Ozempic
How to take Ozempic
Ozempic is typically injected under the skin once weekly with or without food at any time of day. Doctors and healthcare providers recommend that patients take the drug on the same day each week for consistency.
You can inject Ozempic under the skin of the abdominal area (at least 2 inches from your belly button), thigh, or upper arm. It should not be injected into the muscle or vein. Avoid injecting the medication in the same spot for each dose. Instead, you should rotate injection sites.
If you also take insulin, you can inject Ozempic and insulin in the same area of the body. However, avoid mixing insulin and Ozempic in the same injection.
You should also avoid sharing Ozempic pens with others, even if you’ve changed the needle. Sharing the pens carries a risk of spreading or getting a serious infection, like cellulitis, hepatitis, or HIV.
What to do if you miss a dose of Ozempic
Missing a dose of Ozempic is possible, especially since its once-weekly dosing schedule can make it easy to forget. Here’s what to do if you miss a dose:
- If you forget to take your Ozempic dose and your next dose is over 48 hours away, inject the missed dose as soon as you remember.
- If your next dose is due in less than 48 hours, simply wait and continue your regular dosing schedule on the usual day.
- If you skip two or more doses in a row, you can either return to your regular dosing routine or consider restarting Ozempic with the initial dose escalation. Starting at low doses and gradually increasing the dose helps reduce potential gastrointestinal discomfort after restarting treatment.
Other considerations to keep in mind include the following:
- Do not take two doses of Ozempic within 48 hours of each other. Doing so may carry a potential risk of overdose and serious side effects.
- It may be helpful to set reminders or alerts to maintain the dosing schedule and prevent missed doses.
Keeping a weekly Ozempic dose and injection site log can help you keep track of your doses and ensure you rotate injection sites.
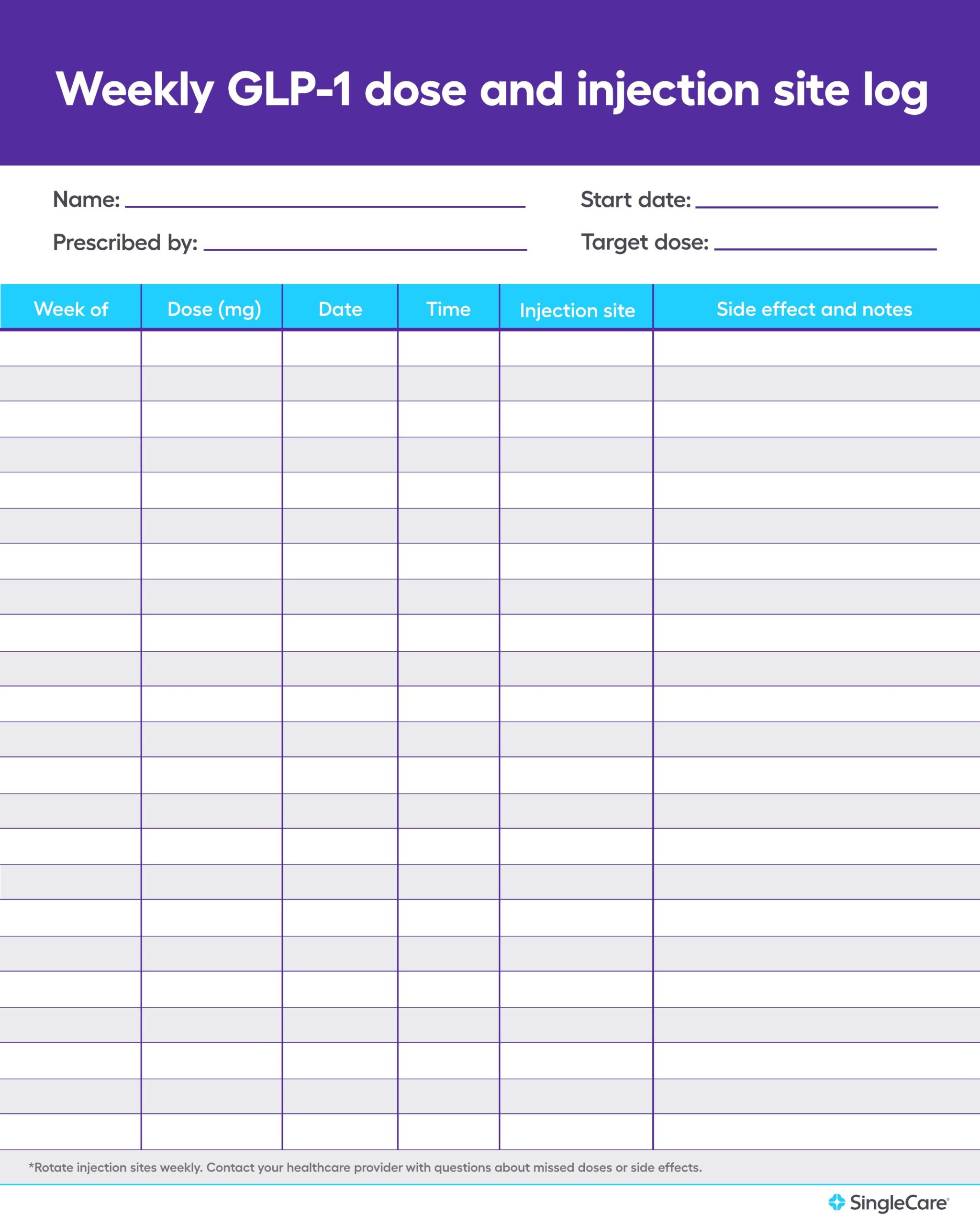
DOWNLOAD THIS GLP-1 DOSAGE CHART FOR FREE
In most cases, missing a dose is not a serious concern. If you habitually miss doses, consult a healthcare provider to determine whether a different medication is necessary. For those who prefer a once-daily oral medication, Rybelsus may be an alternative worth considering since it contains the same active ingredient as Ozempic (semaglutide) in a daily oral form.
- FDA approves first treatment to reduce risk of serious heart problems specifically in adults with obesity or overweight, Food and Drug Administration (2024)
- Ozempic drug label information, DailyMed (2025)
- Can you overdose on Ozempic for weight loss?, Missouri Poison Center (2023)